What is an isometry?
Answer:Transformations that are isometries :
Type of transformation that is not an isometry :
Diagrams of Isometries
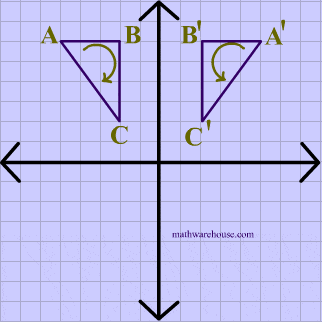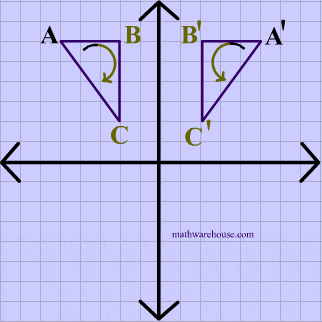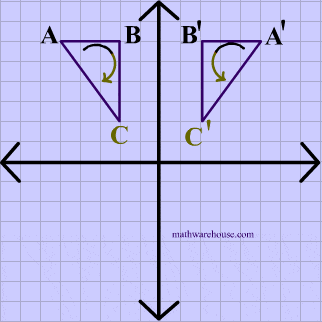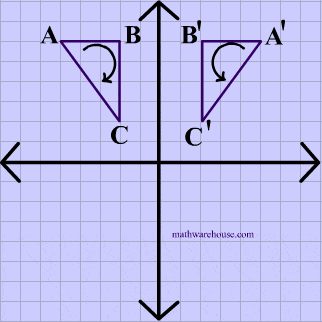
In the diagram below, both the image and the preimage of $$\triangle ABC $$ have the same dimensions, showing that reflections are isometries.
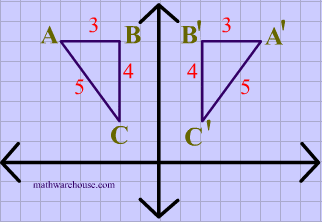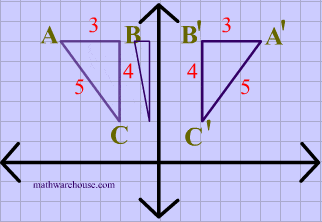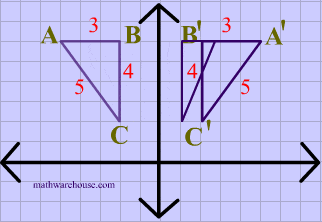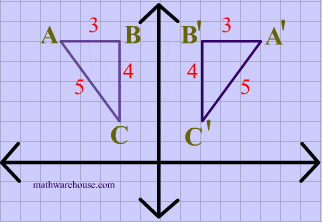
Again in this diagram, both the image and the preimage of $$\triangle ABC $$ have the same dimensions, showing that translations are isometries.
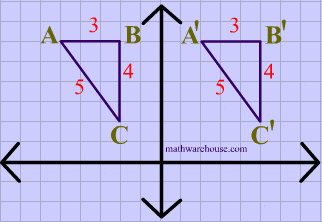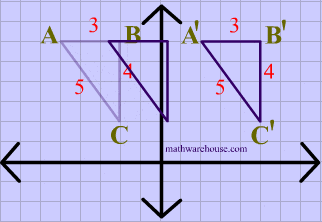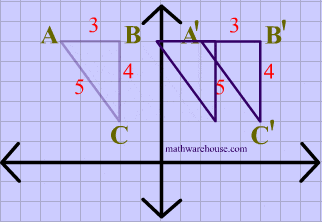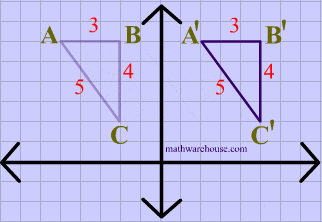
Lastly, both the image and the preimage of $$\triangle ABC $$ have the same dimensions, showing that rotations are isometries.
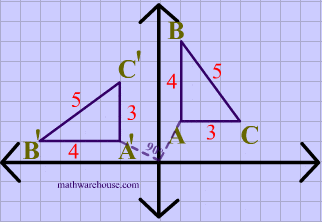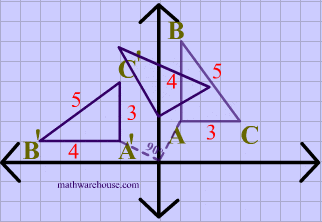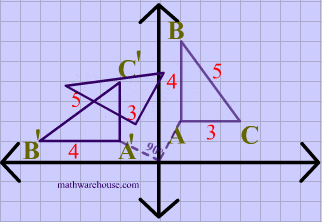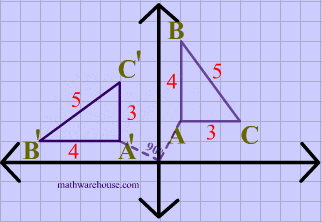
What is a direct isometry?
Answer:Transformations that are direct isometries :
The type of transformations below are not direct isometries :
Direct Isometry Diagrams
The animations below show that rotations and translations are direct isometries because the orientation as well as the distance is preserved.
Rotation Example
In the animation below, the vetices of $$\triangle ABC $$ are in a clockwise order or orientation, and the same is true for the image after the rotation.
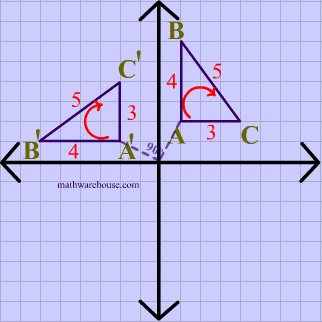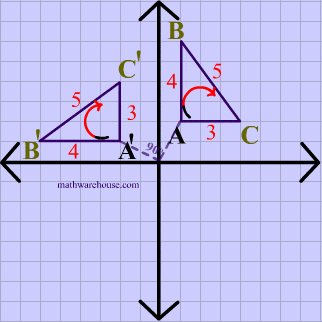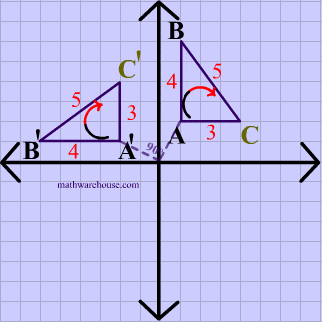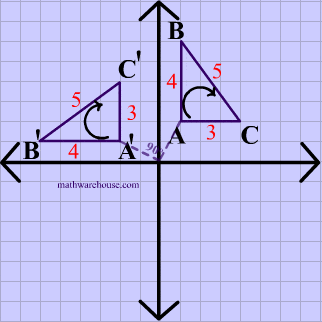
Translation Example
Just like the pior animation, the vetices of $$\triangle ABC $$ are in a clockwise order or orientation, and the same is true for the image after the translation.
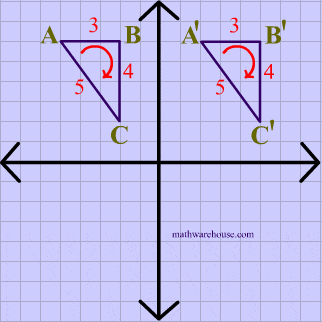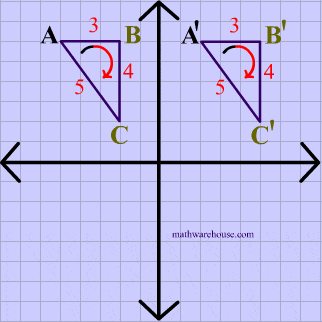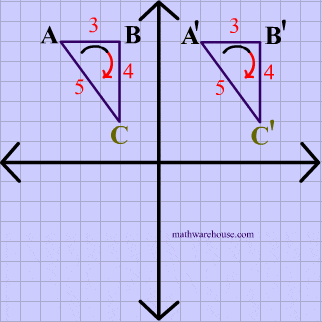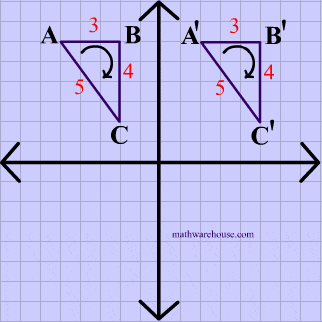
What is an opposite isometry?
Answer:An opposite isometry preserves distance but changes the order, or orientation, from clockwise to counterclockwise, or vice versa.
The one type of transformation that is an opposite isometry is a reflection.
Opposite Isometry Diagram
Reflection Example
The animation below shows that reflections are opposite isometries because the orientation is reversed while the distance is preserved.