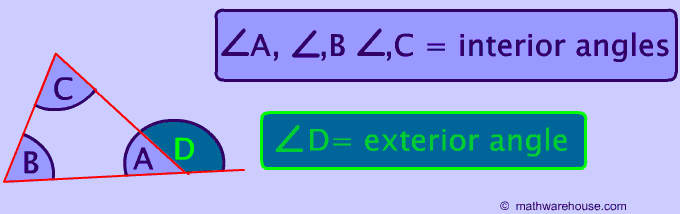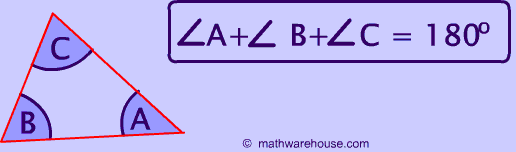Properties of Triangles
Triangles are one of the most fundamental geometric shapes and have a variety of often studied properties including:
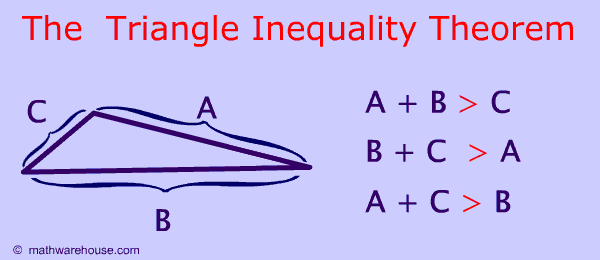

Triangles are one of the most fundamental geometric shapes and have a variety of often studied properties including:
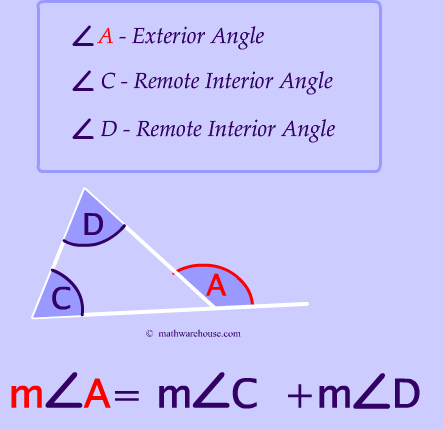
This question is answered by the picture below. You create an exterior angle by extending any side of the triangle.
This may be one the most well known mathematical rules-The sum of all 3 interior angles in a triangle is $$180^{\circ} $$. As you can see from the picture below, if you add up all of the angles in a triangle the sum must equal $$180^{\circ} $$.
To explore the truth of this rule, try Math Warehouse's interactive triangle, which allows you to drag around the different sides of a triangle and explore the relationship between the angles and sides. No matter how you position the three sides of the triangle, the total degrees of all interior angles (the three angles inside the triangle) is always 180°.
This property of a triangle's interior angles is simply a specific example of the general rule for any polygon's interior angles.
| ∠ A | |
| ∠ B | |
| ∠ C | |
| Total | 180 |
|---|
Use the rule for interior angles of a triangle:
m$$ \angle $$ LNM +m$$ \angle $$ LMN +m$$ \angle $$ MLN =180°
m$$ \angle $$ LNM +34° + 29° =180°
m$$ \angle $$ LNM +63° =180°
m$$ \angle $$ LNM = 180° - 63° = 117°
Use the interior angles of a triangle rule:
m$$ \angle $$ PHO = 180° - 26° -64° = 90°
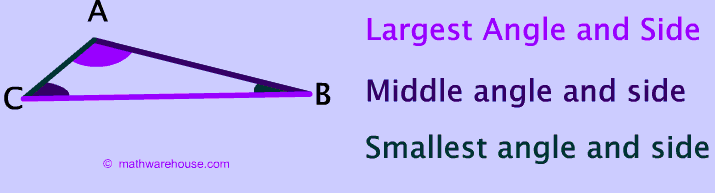
In any triangle
To explore the truth of the statements you can use Math Warehouse's interactive triangle, which allows you to drag around the different sides of a triangle and explore the relationships betwen the measures of angles and sides. No matter how you position the three sides of the triangle, you will find that the statements in the paragraph above hold true.
(All right, the isosceles and equilateral triangle are exceptions due to the fact that they don't have a single smallest side or, in the case of the equilateral triangle, even a largest side. Nonetheless, the principle stated above still holds true. !)