| Solve Quadratic Equations |
The Discriminant |
Composition of Functions |
|
|
100
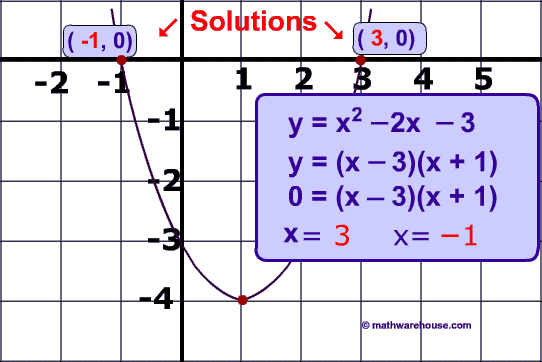
Solve the quadratic Equation Below
y = x2 - 2x - 3
The easiest way to solve this is by factoring:
(x – 3)(x + 1)
x = 3 and x = -1
|
100
Look at the picture below. WHich of the following numbers could be the discriminant of either graph
A) 0
B) -9
C) 10
 III. 10 is the only possible answer since this picture shows a positive discriminant.
III. 10 is the only possible answer since this picture shows a positive discriminant.
|
100
If f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = x – 1
What is (f * g)(2)?
g(2) = 2 – 1 = 1
Now substitue the 1 into f
f(1)= 2(1)+ 3 = 5
|
|
|
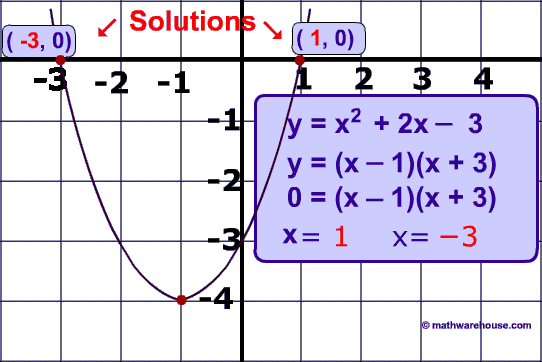
100
Solve the quadratic Equation Below
y = x2 + 2x - 3
Factoring is the easiest method here: (x +3)(x – 1)
x = 1 and x = -3
|
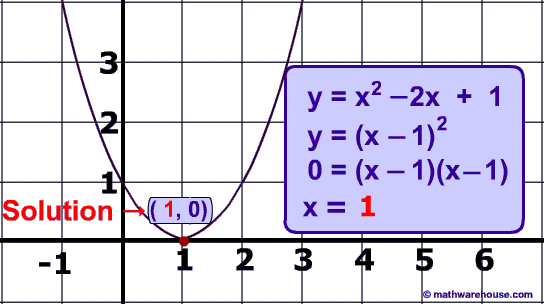
100
Classify the roots of the following equation
y = x - 2x + 1
A) Imaginary
B) Real and Equal
B) Real , Unequal and Irrational
B) Real , Unequal and Rational
a =1
b = - 2
c = 1
Using our general formula, the discriminant is
Disciminant: (-2)2 - 4�1 �1 = 4 - 4 = 0
Since the discriminant is zero,
we should expect 1 real solution which you can see pictured in the graph below.
|
100
If f(x) = 5x + 3 and g(x) = 2x – 1
What is f ( g (3))?
g(3) = 2(3) –1 = 5
f(5) = 5(5) +3 = 28
|
|
|
200
Solve the quadratic Equation Below
y = 9 – x2
This can be factored as a difference of squares
(3 − x)(3 + x)
3 − x = 0  3 = x 3 = x
3 + x = 0  x = - 3 x = - 3
{3, -3}
|
200
Classify the roots of the following equation
y = x2 + 25
A) Imaginary
B) Real and Equal
B) Real , Unequal and Irrational
B) Real , Unequal and Rational
- a =1
- b = 0
- c = 25
- the discriminant = b2 - 4(a)(c) = 02 - 4(1)(25)
- 100 = - 100
Since the discriminant is negative , there are two imaginary solutions to this quadratic equation.
The solutions are 5i and -5i
|
200
If f(x) = 2x and g(x) = x + 1
What is (f * g)(x)
Substitute the entire g(x) in for 'x' in f(x)
f((g(x)) = 2(g(x)) = 2(x+1) = 2x + 2
|
|
|
300
Solve the quadratic Equation Below
y = 32x2 + 8x
Again, this can be factored :
0 = 32x2 + 8x
0 = 8x(4x + 1)
8x = 0  x = 0 x = 0
4x + 1 = 0  x = - ¼ x = - ¼
|
200
Is the equation below a relation, a function, or a 1 to 1 function?
9x2 + 4y2=36
Relation. This is the equation of an ellipse and doesn't pass the vertical or horizontal line tests .
|
200
If f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x – 1
What is (g* f)(x)
g(f(x)) = (x2) – 1
|
|
|
300
Solve this quadratic Equation
y = x2 - 4x + 5 and its solution
This quadratic equation has imaginary roots.
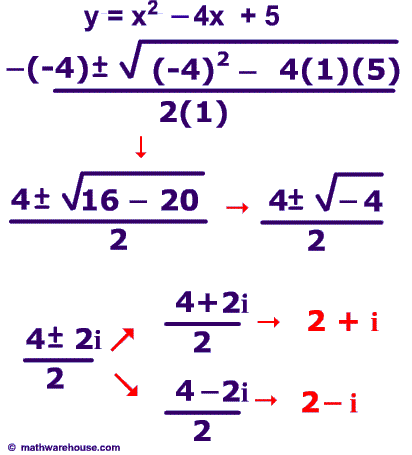
|
300
Is the equation below a relation, a function, or a 1 to 1 function?
xy = 11
1 to 1 function this is the one type of hyperbola that is a 1 to 1 function.
|
300
The accompanying tables define functions f and g
What is (g * f)(3)?
f(3) = 5
g(5) = 8
|
|
|













