
|
 
  
 |
How to Declare and Initialize ArraysString[], int[] and double[]
Part I: How to Declare and Initalize an Array
You can declare an array of any type. Below we create an array of ints and we only initialized the first three values. 
Below is an example of an array of Strings. This array can store 400 Strings! We only used the first three spots.
String[] anArrayofStrings = new String[400]; anArrayofStrings[0] = "1" ; anArrayofStrings[1] = "aldjlajld;"; anArrayofStrings[2] = "djka"; Uninitalized elements : In our example above there are 397 slots that we haven't yet inialized. The default value of an uninitalized element is null. See the example below The Length Property of Arrays

Run the loop below to understand what it does.
int[] anArrayOfints = new int[100];
for(int i = 0;i< anArrayOfints.length; i++){
anArrayOfints[i] = i*3;
}
for(int i = 0;i< anArrayOfints.length; i++){
System.out.println(anArrayOfints[i]) ;
}
How to loop over an Array in JavaThe general method for looping through an array is similar to how you loop through a String . In both cases, you use the length of the object and an index value based on a loop. 
Below are two different loops. Each one iterates over the entire array. If you're familiar with the % operator, you should be able to figure out what the programmer below was trying to do: to print out all of the elements that are divisible by 10. However, only one of the loops actually does this. Can you determine which loop works properly.
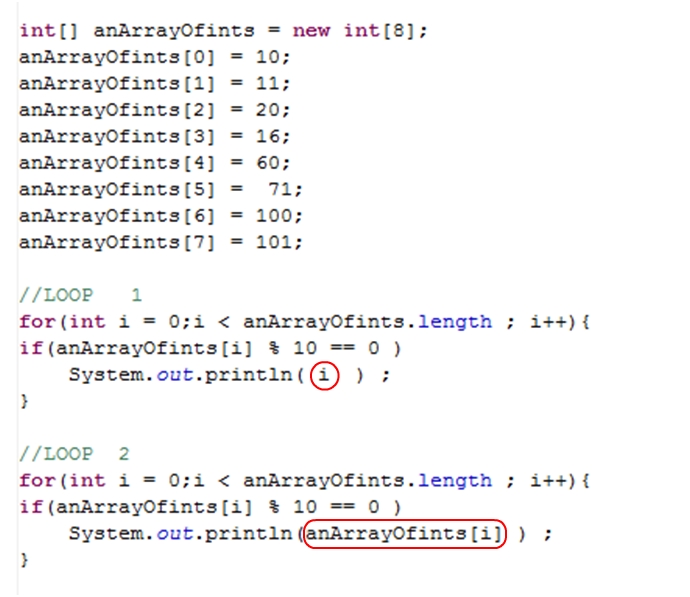
Often times you want to compare elements within an array to try to figure somethign out. Look at the loop below. What is this loop 'figuring out' about the array of ints 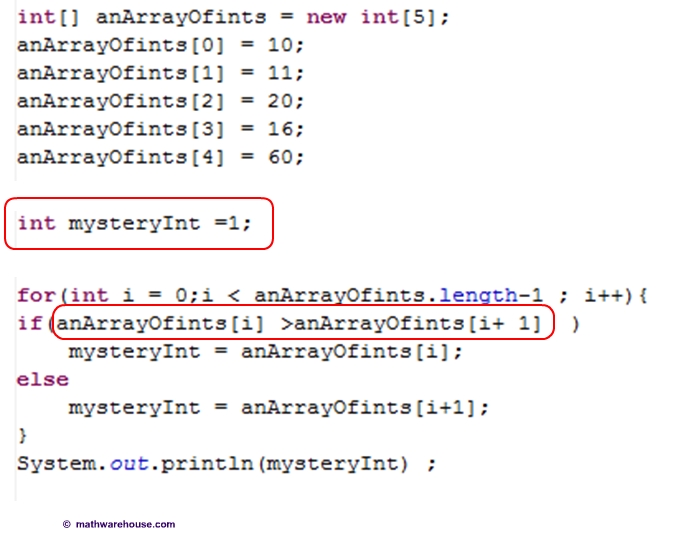
Deadline: The last day that we will have class time dediated to solving thse will be Friday.
|