This page : Lesson | Practice | Complex Conjugates
Just like multiplying binomials
To multiply two complex numbers such as ( 4 + 5 i ) ⋅ ( 3 + 2 i ) binomial
and apply the foil method to find the product.
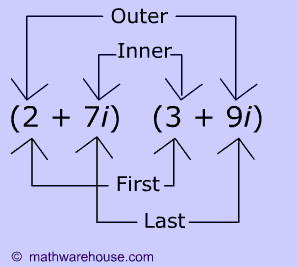
FOIL stands for
first ,
outer ,
inner , and
last
pairs. You are supposed to multiply these pairs as shown below!
Note: the i 2 simplifies to − 1
So, now that we've multiplied, what is next?
Add up each term!
Content on this page requires a newer version of Adobe Flash Player.
Video Tutorial on Multiplying Complex Numbers
VIDEO
Example 1
Let's multiply the following 2 complex numbers ( 5 + 2 i ) ( 7 + 12 i )
Step 1
Foil the binomials.
F ( 5 + 2 i ) ( 7 + 12 i ) 5 ⋅ 7 35 O ( 5 + 2 i ) ( 7 + 12 i ) 5 ⋅ 12 i 60 i I ( 5 + 2 i ) ( 7 + 12 i ) 2 i ⋅ 7 14 i L ( 5 + 2 i ) ( 7 + 12 i ) 5 i ⋅ 12 i 24 i 2 = − 24
Remember i 2 = − 1 24 i 2 = 24 ⋅ − 1 = − 24
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
This page : Lesson | Practice | Complex Conjugates
Practice Problems I
Problem 1.1
Step 1
Step 1 answer
F ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 6 + 4 i ) 5 ⋅ 6 30 O ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 6 + 4 i ) 5 ⋅ 4 i 20 i I ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 6 + 4 i ) 4 i ⋅ 6 24 i L ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 6 + 4 i ) 4 i ⋅ 4 i − 16 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ] i 2 = − 1 4 i ⋅ 4 i = 16 i 2 = 16 ⋅ − 1 = − 16
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
Problem 1.2
Step 1
Step 1 answer
F ( 9 + 7 i ) ( 6 + 8 i ) 9 ⋅ 6 54 O ( 9 + 7 i ) ( 6 + 8 i ) 9 ⋅ 8 i 72 i I ( 9 + 7 i ) ( 6 + 8 i ) 7 i ⋅ 6 42 i L ( 9 + 7 i ) ( 6 + 8 i ) 7 i ⋅ 8 i 56 i 2 = − 56
Remember i 2 = − 1 56 i 2 = 56 ⋅ − 1 = − 56
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
Step 2 answer
54
72 i
42 i
+ ( − 56 )
− 2 + 114 i
Problem 1.3
Step 1
Step 1 answer
F ( 2 − 4 i ) ( 3 + 5 i ) 2 ⋅ 3 6 O ( 2 − 4 i ) ( 3 + 5 i ) 2 ⋅ 5 i 10 i I ( 2 − 4 i ) ( 3 + 5 i ) − 4 i ⋅ 3 − 12 i L ( 2 − 4 i ) ( 3 + 5 i ) − 4 i ⋅ 5 i − 20 i 2 = 20
Remember i 2 = − 1 − 20 i 2 = − 20 ⋅ − 1 = 20
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
This page : Lesson | Practice | Complex Conjugates
Complex Conjugate
Complex conjugates are any pair of complex number
binomials that look like the following pattern:
( a + b i ) ( a − b i )
Here are some specific examples. Note that the only difference between the two binomials is the
sign .
Complex Conjugate Examples
( 3 + 2 i ) ( 3 − 2 i ) ( 5 + 12 i ) ( 5 − 12 i ) ( 7 + 33 i ) ( 5 − 33 i ) ( 99 + i ) ( 99 − i )
Multiplying complex conjugates causes the middle term ( the i example 2 below illustrates.
Example 2 (Complex Conjugate)
Let's multiply 2 complex conjugates ( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i )
Step 1
Foil the binomials.
F ( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i ) 4 ⋅ 4 16 O ( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i ) 4 ⋅ − 6 i − 24 i I ( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i ) 6 i ⋅ 4 24 i L ( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i ) 6 i ⋅ − 6 i 36 [ 1 ]
[ 1 ] i 2 = − 1 − 36 i 2 = − 36 ⋅ − 1 = 36
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
(notice how the imaginary terms are
additive inverses
or 'cancel' each other)
Shortcut for Multiplying Complex Conjugates
There is a shortcut that you can use to quickly multiply complex conjugates.
As you can see from the last example.
( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i ) = 16 + 36 ( 4 + 6 i ) ( 4 − 6 i ) = 4 2 + 6 2
Shortcut:
( a + b i ) ( a − b i ) = a 2 + b 2
Problem 2.1
Step 1
Step 1 answer
F ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 5 − 4 i ) 5 ⋅ 5 25 O ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 5 − 4 i ) 5 ⋅ − 4 i − 20 i I ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 5 − 4 i ) 4 i ⋅ 5 20 i L ( 5 + 4 i ) ( 5 − 4 i ) 4 i ⋅ − 4 i − 16 i 2 = 16
Remember i 2 = − 1 − 16 i 2 = − 16 ⋅ − 1 = 16
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
Step 2 answer
Shortcut: There is a shortcut that applies to complex conjugates of the form
( a + b i ) ( a − b i ) a 2 + b 2 5 2 + 4 2
Problem 2.2
Step 1
Step 1 answer
F ( 6 + 2 i ) ( 6 − 2 i ) 6 ⋅ 6 36 O ( 6 + 2 i ) ( 6 − 2 i ) 6 ⋅ − 2 i − 12 i I ( 6 + 2 i ) ( 6 − 2 i ) 2 i ⋅ 6 12 i L ( 6 + 2 i ) ( 6 − 2 i ) 2 i ⋅ − 2 i − 4 i 2 = 4
Remember i 2 = − 1 − 4 i 2 = − 4 ⋅ − 1 = 4
Step 2
Simplify by adding the terms
Step 2 answer
Shortcut: There is a shortcut that applies to complex conjugates of the form
( a + b i ) ( a − b i ) a 2 + b 2 6 2 + 2 2
Problem 2.3
Step 1
Answer
Use the shortcut to rewrite the left side.
( 1 + a i ) ( 1 − a i ) = 2 1 2 + a 2 = 2 1 + a 2 = 2 a 2 = 1 a = √ 1 a = 1